Hemorrhoids, often known as piles, are a common issue. These swollen veins inside or outside of the rectum can cause pain, itching in the anus, and bleeding in the rectal area. Even while at-home treatments usually lead to better symptoms, people occasionally need to have medical procedures done. Consuming more fiber can aid in preventing hemorrhoids.
Overview
What are hemorrhoids?
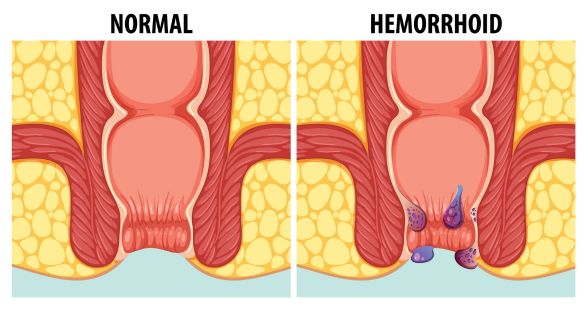
Hemorrhoids are swollen, enlarged veins that occur both inside and outside the anus and rectum. They hurt and are uncomfortable, and they could cause rectal bleeding. Hemorrhoids are sometimes known as piles. Although they are a normal aspect of being human, hemorrhoids usually don’t bother us. They swell and expand before they begin to create uncomfortable symptoms.
How common are hemorrhoids?
It is estimated that 1 in 20 Americans suffers from hemorrhoids. People of all ages, genders, races, and ethnicities are impacted by them. Over half of those over 50 are affected by them, and their frequency increases with age.
Who might get hemorrhoids?
Hemorrhoids can affect anyone, even teenagers. (However, hemorrhoids are rare in children since they take time to develop.) You might be more vulnerable if you:
1. Have overweight/obesity.
2. Are pregnant.
3. Eat a low-fiber diet.
4. Have chronic diarrhea or constipation.
5. Regularly lift heavy objects.
6. Sit on the toilet for extended periods of time.
7. Put strain on your bowel movements.
What are the types of hemorrhoids?
You may get hemorrhoids inside or outside of your rectum. The location of the enlarged vein determines the kind. Types consist of:
1. External: Veins under your skin swell around your anus. The tube where your excrement exits is called your anus. Hemorrhoids on the outside can hurt and itch. Every now and then, they bleed. They occasionally fill with clotting blood. Although not harmful, this may cause discomfort and edema.
2. Internal: Veins inside your rectum swell. The portion of your digestive system that joins your anus and colon (large intestine) is called the rectum. Internal hemorrhoids are usually not uncomfortable, despite the possibility of bleeding.
3. Prolapsed: Hemorrhoids can prolapse, or extend and bulge outside of your anus, both internal and external. These hemorrhoids could hurt or bleed.
What’s the difference between hemorrhoids and anal fissures?
Hemorrhoids and anal fissures are both commonly accompanied by itching, pain, and bleeding. An anal fissure is caused by a tear in the lining of your anus, whereas hemorrhoids are caused by bulging veins. To identify the cause of your symptoms, a medical professional may examine you physically and may prescribe tests.
Symptoms and Causes
What causes hemorrhoids?
Hemorrhoids are caused by straining, which puts pressure on the veins in your rectum or anus. Consider them to be varicose veins on your lower limbs.
Anal and rectal veins can swell and become inflamed with any type of straining that puts more pressure on your abdomen or lower extremities. Hemorrhoids may appear as a result of:
1. Weight growth, particularly during pregnancy, can cause pelvic discomfort.
2. Pushing excessively to pass gas (poop) in order to alleviate constipation.
3. Bending over to lift large things or performing weightlifting.
What are the symptoms of hemorrhoids?
Unless they prolapse, internal hemorrhoids rarely hurt and are usually not perceptible. Since internal hemorrhoids don’t cause any symptoms, a large number of people are unaware that they even have them.
Blood on toilet paper, in your stool, or in the toilet bowl could be signs of internal hemorrhoids. These indicate rectal hemorrhage.
Signs of external hemorrhoids include:
1. Itchy anus.
2. Rectal bleeding.
3. Hard, sensitive, uncomfortable bumps close to your anus.
4. Anus pain or soreness, particularly while sitting.
Hemorrhoids that have prolapsed can be uncomfortable and painful. Gently push them back inside, if you can feel them protruding outside of your anus.
What other illnesses result in symptoms similar to hemorrhoids?
Hemorrhoids-like symptoms, such as rectal bleeding, can be caused by many gastrointestinal illnesses. A few of these illnesses pose a serious risk to life. It’s crucial that you inform a healthcare professional of your symptoms because of this.
Bowel diseases that can cause bleeding include:
1. Crohn’s disease.
2. Colon cancer.
3. Ulcerative colitis.
Diagnosis and Tests
How are hemorrhoids diagnosed?
Hemorrhoids are diagnosed by a medical professional based on a physical examination and symptoms. You might additionally have:
1. Digital rectal exam: To check for enlarged veins, your healthcare professional will stick a gloved, lubricated finger into your rectum.
2. Anoscopy: Your doctor views the lining of your rectum and anus using an anoscope.
3. Sigmoidoscopy: Your doctor views the lower (sigmoid) portion of your colon and rectum using a sigmoidoscope. There are two types of procedures: rigid sigmoidoscopy and flexible sigmoidoscopy.
Although they may cause discomfort, these exams are not painful. They usually happen without anesthetic at an outpatient facility or doctor’s office. Same day, you head back home.
To confirm results from earlier tests or look for indications of colon cancer, your doctor might do a colonoscopy. For this outpatient procedure, anesthesia is necessary.
Management and Treatment
What are the complications of hemorrhoids?
Hemorrhoids can be painful and uncomfortable, hemorrhoids usually don’t result in major issues. Hemorrhoids seldom cause persons to develop:
1. Infection.
2. Anemia.
3. Skin tags (flap of tissue that hangs off skin).
4. Blood clots in external hemorrhoids.
5. Strangulated hemorrhoids.
How can I treat hemorrhoids at home?
Often, hemorrhoids disappear on their own without medical treatment. Pain and bleeding symptoms could linger for a week or a little longer. In the interim, you can reduce symptoms by doing the following steps:
1. On the affected area, apply over-the-counter drugs like hydrocortisone, witch hazel, or lidocaine.
2. Drink more water.
3. Soften stool by taking laxatives.
4. Boost your diet of fiber with food and supplements. Make an effort to consume 20 to 35 grams of fiber every day.
5. Spend 10 to 20 minutes per day in a warm bath (sitz bath).
6. Take nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) for pain and inflammation.
7. After you’ve pooped, gently pat and clean your behind with toilet paper soaked in lotion or flushable wet wipes. Another option is to use a tissue or washcloth soaked in water. Wipes should be thrown in the garbage rather than flushed. To stop illnesses that are frequently found in feces from spreading, washcloths separately in hot water.
How do healthcare providers treat hemorrhoids?
If your symptoms worsen or start to affect your everyday activities or ability to sleep, you should consult your doctor. In addition, get assistance if symptoms worsen despite a week of at-home therapy. Hemorrhoids may be treated by your doctor using:
1. Rubber band ligation: A tiny rubber band wrapped around the base of a hemorrhoid stops the vein’s blood supply.
2. Electrocoagulation: Blood flow to a hemorrhoid is stopped by an electric current.
3. Infrared coagulation: To remove the hemorrhoid, a little probe that is put into the rectum emits heat.
4. Sclerotherapy: Hemorrhoid tissue is destroyed by a chemical that is injected into the enlarged vein.
Surgical treatments include:
1. Hemorrhoidectomy: Large external hemorrhoids and prolapsed internal hemorrhoids are removed surgically.
2. Hemorrhoid stapling: An internal hemorrhoid is removed with a stapling tool. Alternatively, it keeps a prolapsed internal hemorrhoid inside your anus after pulling it back.
Prevention
How can I prevent hemorrhoids?
As you age, hemorrhoids become more frequent. The following actions might lessen the risk of constipation and firm stools, which can result in hemorrhoids:
1. Avoid overusing the toilet seat or pushing too hard.
2. When the desire strikes, don’t delay bowel movements.
3. Drink Water is your best beverage throughout the day.
4. Eat more whole grains, fruits, and vegetables, as well as other high-fiber foods; alternatively, consider taking supplements. In general, individuals identified as male at birth should consume 35 grams of fiber daily, while women and those labeled as female at birth should strive for 25 grams.
5. Continue your physical activity. Bowel movements are maintained by movement.
6. Only use laxatives or utilize enemas as directed by your physician. The overuse of laxatives or enemas can interfere with the body’s ability to control bowel movements.
Outlook / Prognosis
What is the prognosis, or outlook, for hemorrhoidal patients?
With at-home remedies, hemorrhoid symptoms typically resolve within a week. Surgery or other medical procedures may be helpful if hemorrhoids are causing excruciating pain and discomfort.
Living With
When should I call the doctor?
If you suspect hemorrhoids and encounter any of the following symptoms, you should see your doctor:
1. Fever and chills.
2. Abdominal pain.
3. Nausea and vomiting.
4. Chronic constipation or diarrhea.
5. Severe rectal bleeding and pain.
What questions should I ask my doctor?
You should ask your medical professional:
1. Why did I get hemorrhoids?
2. What’s the best treatment for me?
3. When will symptoms improve?
4. Should I keep an eye out for any indications of trouble?
5. What lifestyle adjustments can I do to prevent hemorrhoids from occurring again?
A note from Blogjug
At some time in their lives, an estimated 15 million Americans have sought treatment for hemorrhoids. But they unnecessarily affect a great number of others. Don’t be afraid to discuss your symptoms with your healthcare physician. Your healthcare practitioner might offer therapies to help if hemorrhoids are causing you pain or discomfort. Additionally, you can take action to prevent hemorrhoids from returning.








